TSMC’s fourth‑quarter 2025 financial results paint a vivid picture of a company operating at the centre of the global semiconductor ecosystem, where demand for advanced chips continues to reshape both its financial trajectory and the broader technology landscape. The quarter was marked by strong revenue growth, expanding margins, and a clear affirmation that artificial intelligence and high‑performance computing have become the dominant forces driving the foundry’s momentum.
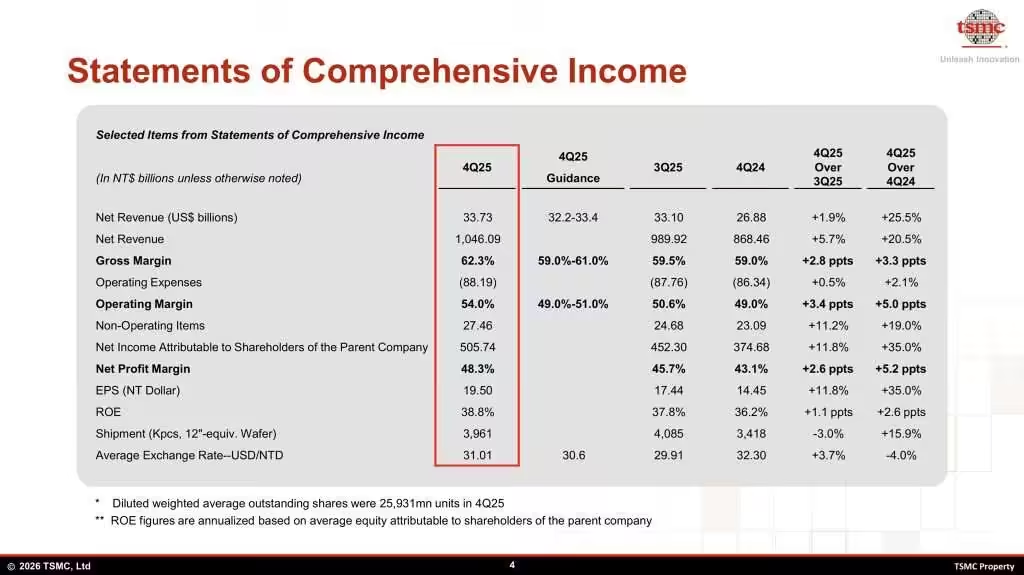
The company reported consolidated revenue of US$33.73 billion, representing a 25.5 percent year‑over‑year increase and a modest sequential rise from the previous quarter. In local currency terms, revenue reached NT$1.046 trillion, crossing the trillion‑dollar mark for the first time in a fourth quarter and underscoring the scale at which TSMC now operates. This performance exceeded market expectations and reflected the sustained strength of AI‑related demand, even as consumer electronics markets remained comparatively subdued.
Profitability also strengthened meaningfully. TSMC posted a gross margin of 62.3 percent and an operating margin of 54 percent, both improvements from earlier in the year and well above historical averages for the semiconductor foundry industry. Net income rose 35 percent year‑over‑year to TWD 505.7 billion, or roughly US$16 billion, highlighting the leverage that advanced manufacturing nodes continue to provide as utilization remains high and cost‑reduction efforts take effect.
A defining feature of the quarter was the continued dominance of leading‑edge process technologies. Shipments of 3‑nanometer chips accounted for 28 percent of total wafer revenue, while 5‑nanometer contributed 35 percent and 7‑nanometer added 14 percent. Taken together, technologies at 7 nm and below represented 77 percent of total wafer revenue, a figure that illustrates how deeply the industry has shifted toward advanced nodes as the foundation for AI accelerators, cloud infrastructure, and next‑generation mobile devices. This concentration also reflects TSMC’s strategic position as the primary manufacturing partner for companies like Nvidia, Apple, AMD, and Broadcom, all of whom rely on the foundry’s most sophisticated processes.
The platform mix further reinforces this trend. High‑performance computing accounted for 55 percent of TSMC’s Q4 revenue, far surpassing the contribution from smartphones and marking a structural shift in the company’s revenue base. AI accelerators alone represented a high‑teens percentage of total revenue for the full year, according to management commentary, and this share is expected to rise as cloud providers continue to secure long‑term capacity for their data‑centre roadmaps. The company’s leadership has repeatedly described AI as a multi‑year megatrend, and the fourth‑quarter results provide quantitative evidence of that conviction.
The quarter also highlighted the growing complexity and cost of manufacturing at the leading edge. TSMC noted that capital expenditures for 2026 are expected to fall between US$52 billion and US$56 billion, up sharply from US$40.9 billion in 2025, reflecting the rising cost of tools, the challenges of scaling 2‑nanometer production, and the expansion of global manufacturing footprints. Executives emphasized that building capacity for 2 nm requires substantially higher investment per 1,000 wafers than 3 nm, and that future nodes such as 1.4 nm will be even more capital‑intensive. These comments underscore the escalating financial demands of staying at the forefront of semiconductor manufacturing.
Geographically, revenue contributions remained diversified, with Japan and the EMEA region each accounting for about four percent of total revenue, according to external reporting. While these shares are relatively small, they reflect the broader global demand for advanced chips and the increasing importance of regional supply‑chain strategies. TSMC’s ongoing expansion in the United States, particularly in Arizona, also featured prominently in management discussions. The company confirmed that construction of its third fab has begun and that it is applying for permits for a fourth fab and an advanced packaging facility, signalling a long‑term commitment to building a multi‑fab cluster in the region.
Despite the strong results, TSMC’s leadership acknowledged the uncertainties inherent in the rapid growth of AI‑related demand. When asked whether the industry might be experiencing a bubble, Chairman C.C. Wei noted that he remains cautious but emphasized that conversations with major customers continue to reinforce the view that AI demand is real and durable. This balanced perspective reflects both the extraordinary pace of AI infrastructure build‑out and the need for disciplined capacity planning to avoid over‑investment.
Looking ahead, the company expects first‑quarter 2026 revenue to reach between US$34.6 billion and US$35.8 billion, representing up to 38 percent year‑over‑year growth at the high end of the range. Gross margins are projected to remain strong at 63 to 65 percent, supported by continued demand for leading‑edge technologies and favourable utilization trends. These forecasts suggest that the momentum seen in Q4 is likely to carry into the new year, driven by the same structural forces that shaped the quarter’s performance.
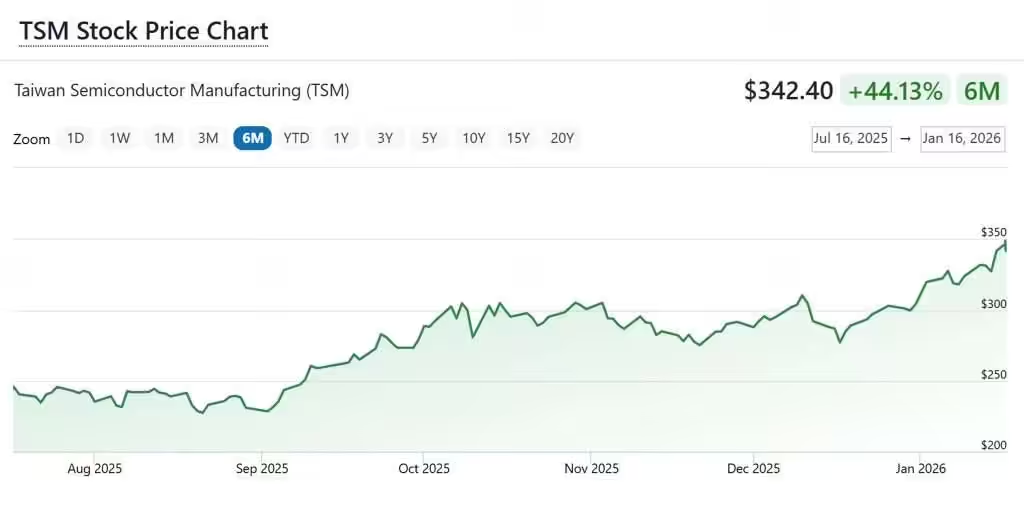
TSMC Share Price (NYSE:TSM)
TSMC’s share price has been surging as investors respond to a powerful combination of booming AI demand, stronger‑than‑expected earnings, and increasingly bullish analyst outlooks. In early January, the stock jumped as much as 6.9 percent in Taipei after Goldman Sachs raised its price target by 35 percent, citing AI as a “multi‑year growth engine” for the company. The rally pushed TSMC’s market value above US$1 trillion, a milestone that reflects how central the company has become to the global semiconductor supply chain. Momentum continued after TSMC released its Q4 2025 results, which beat expectations on both revenue and margins, triggering another wave of buying as markets interpreted the numbers as validation of the AI infrastructure boom. With advanced nodes now accounting for the vast majority of its wafer revenue and demand from Nvidia, AMD, and Apple showing no signs of slowing, TSMC’s share price has become a barometer for the broader AI‑driven semiconductor cycle.
Conclusion on TSMC Q4 2025 Results
TSMC’s fourth‑quarter 2025 results ultimately reflect a company operating at the intersection of technological ambition and global economic transformation. The surge in AI‑related demand has reshaped its revenue mix, elevated its margins, and accelerated its capital‑expenditure plans. At the same time, the challenges of scaling ever‑smaller nodes, managing global expansion, and navigating uncertain macroeconomic conditions remain significant. Yet the quarter demonstrates that TSMC continues to meet these challenges with a combination of technical leadership, operational discipline, and strategic clarity.